
5 Reasons to Use Zero Trust Architecture
At a high level, Zero Trust Architecture can be summed up by the phrase “never trust, always verify.” This means that the detection and prevention for each component can improve assurance for the system as well as the software while defending against malicious actors. According to NIST, Zero Trust is defined as “a collection of concepts and ideas designed to minimize uncertainty in enforcing accurate, least privilege per-request access decisions in information systems and services in the face of a network viewed as compromised.” Under a Zero Trust framework, security properties are verified dynamically to ensure that the expected authentication and verification controls are met. Each component that is built with Zero Trust in mind is engineered to recognize if the adjoining or adjacent components may possess any vulnerabilities. Seeing as how each individual component in a stack comes with its own trust level, it may be able to detect an attempted attack or possible compromise before it occurs.
So how can your IT teams manage the deployment and implementation of a Zero Trust Architecture and still maintain assurance of its effectiveness? Let’s break it down.
Principles of Zero Trust
In general, most zero trust architectures are made up of a complex combination of infrastructure, firmware, software and data that relies on the isolation of parts or services from one another for infrastructure assurance. According to information released in the NIST CSRC publication SP 800-207, some of the main points behind Zero Trust include:
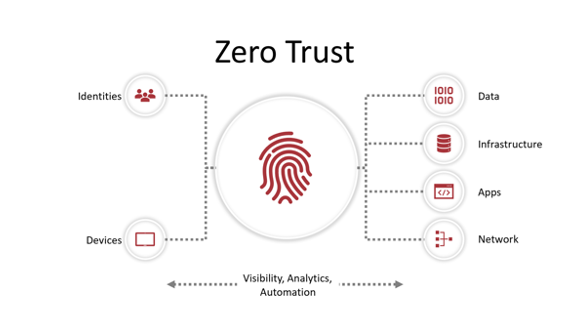
- Access to resources is determined by dynamic policy
- All communication is secured regardless of location
- Access to individual enterprise resources is granted on a per-session basis
- All data sources and computing services are considered resources
- All owned and associated devices are in the most secure state possible
- All resource authentication and authorization are dynamic and strictly enforced
- Collect as much information as possible on current state of network infrastructure to improve security posture
By applying the most extreme security controls possible to anything your team may be working on (data, infrastructure, apps, network) you are removing any accountability the end user may have, therefore establishing the model known as “Zero Trust.”
The Benefits
Zero Trust can manage user access to applications, data and devices while improving visibility and control. There are many benefits to implementing a Zero Trust framework, including increasing visibility, reducing dwell time and providing consistent proof that your data is safe and sound. Based on research into the data-centric world of endpoint security, here are five key reasons to use Zero Trust:
- Proven to Work
- Many businesses rely on Zero Trust Architecture to maintain their integrated, end-to-end security posture. Zero Trust can help identify security vulnerabilities with unified endpoint management that’s proven to work in multiple-use cases.
- Simplified Security Solutions
- Any organization can streamline and strengthen their cloud security by using Zero Trust to replace disparate products with a scalable security framework that consolidates endpoint detection, response and protection into one. Zero Trust can also be applied across multiple systems while enabling more secure identity and access management.
- Reduced IT Costs
- Forrester Research found that Zero Trust can mitigate an organization’s risk exposure by at least 37 percent and reduce security costs by 31 percent, saving not only time and money but wasted energy on unnecessary IT expenditures.
- Improved User Behavior
- Zero Trust forces users to be secure at all levels of connecting to company data. They will naturally compare what they do with other parts of their life and hopefully, improve their security posture.
- Reinforce Best Practices
- Instead of IT teams submitting a request to open a firewall port to a particular address, Zero Trust allows users to investigate their request directly, assess what it will be used for and who uses it.
Due to the increasing complexity of network environments and the ability of malicious actors to compromise them, implementing Zero Trust requires a change in defensive strategy, as well as a shift in focus. According to the National Security Agency, using a Zero Trust model to secure a data center, public cloud and endpoints can definitively prevent the propagation of a ransomware attack, which subsequently reduces downtime for a business. The Zero Trust mindset focuses on securing critical data and access paths by eliminating trust as much as possible, coupled with verifying and regularly re-verifying every allowed access. However, implementing Zero Trust should not be taken lightly and will require significant resources and persistence to achieve.
When properly implemented, Zero Trust can prevent, detect and contain threats faster and more effectively than the more traditional cybersecurity architectures currently still held in place by many organizations. To stay safe in a world of evolving and ever-present dangers, companies can start proactively detecting the malicious threats of tomorrow before they occur by implementing a Zero Trust model today.

written by
Red River
We call ourselves a technology transformation company because we know how to harness the power of technology to change the way you do business and meet mission objectives. Our industry leading technical expertise, strategic partnerships and portfolio of services and solutions that span the entire lifecycle of technology have made us the partner of choice for clients in the commercial, federal and SLED markets interested in optimizing business processes and maximizing the value of their investments. Learn more about Red River.




